Visa-Sponsored Workers in the US Must Comply with New Biometric Registration
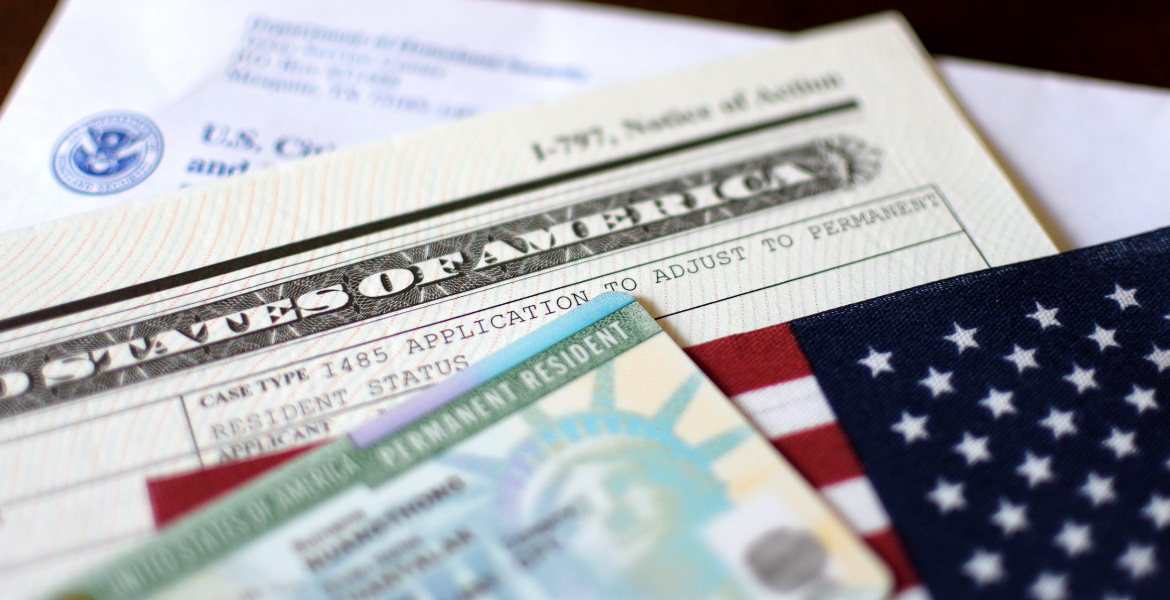

Starting January 20, 2025, US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) will enforce new alien registration requirements, impacting numerous non-US citizens residing in the United States.
The regulation mandates fingerprinting and registration for many foreign nationals, reinforcing longstanding immigration compliance measures. This policy shift primarily affects those who did not undergo fingerprinting during their initial US visa application and who remain in the country for 30 days or more. This policy underscores a pivotal aspect of US immigration law, which, though present in various forms previously, is now subject to more stringent enforcement. Non-compliance could lead to penalties, including fines of up to $5,000 and potential imprisonment, emphasising the urgency of adhering to the registration timeline.
Who Must Register?
The new guidelines stipulate that foreign nationals aged 14 and above must register if their fingerprints were not collected during the visa application process. Minors turning 14 while residing in the US are required to register within 30 days of their birthday. This rule also encompasses Canadians entering the US via land borders who do not receive official documentation confirming their registration.
Exemptions apply to lawful permanent residents and those holding specific visa classifications, such as individuals with Employment Authorisation Documents (EADs) or a valid Form I-94 issued upon arrival. USCIS has clarified that applicants who have already provided biometrics during their visa application are considered registered, eliminating the need for redundant processes.
Navigating the Registration Process
USCIS has established a structured, digital-first process for those required to comply. The initial step involves creating a personal USCIS online account, which is essential for submitting Form G-325R, the biographic information form necessary for registration. Each individual must file Form G-325R separately through their personal USCIS account. This includes minors under 14, for whom parents or legal guardians must complete the registration. The exclusively online format reflects USCIS’s broader initiative to digitise immigration management, eliminating the options for traditional mail-in or in-person submissions.
Upon submission, USCIS will review the applicant’s information and cross-reference it with existing records to determine whether registration is necessary. If previous biometric data is available, USCIS may confirm compliance without requiring further action. However, individuals who need to provide fingerprints will be scheduled for an appointment at designated Application Support Centres.
Failure to attend a scheduled biometric appointment constitutes a serious violation of immigration law, potentially leading to criminal penalties. The agency stresses the importance of adhering to scheduled appointments to avoid complications that could jeopardise future immigration benefits or visa extensions.
Proof of Registration and Documentation Requirements
Upon successful registration and biometric submission, registrants will receive official documentation via their online USCIS account. Foreign nationals aged 18 and above must carry this proof of registration at all times. Acceptable forms of registration documentation include Form I-94, a valid Employment Authorisation Document, or a foreign passport bearing an unexpired DHS admission stamp. USCIS affirms that documentation will be necessary for various legal interactions, including applications for benefits and future visa renewals.
Change of Address Notification
A critical element of immigration compliance, and an often overlooked requirement, is notifying USCIS of any change in residential address. Under the new rule, non-citizens must report any change within 10 days to remain compliant. Non-compliance can result in fines and imprisonment, with potential ramifications for future immigration proceedings. The notification requirement ensures that immigration records are current, allowing the US government to maintain accurate information on non-citizens residing within its borders. While non-willful failures to report changes may be excused, individuals bear the responsibility for ensuring timely notifications.
The Broader Implications of the Policy
The updated registration protocol aligns with broader national security and immigration enforcement strategies, reinforcing accountability among visa holders. By implementing a digital registration process, USCIS aims to streamline record-keeping while tightening compliance measures. Understanding these requirements is essential for foreign nationals, not only to avoid legal penalties but also to ensure seamless interactions with US immigration authorities.
The policy is particularly relevant for individuals entering the country on visas who may not be familiar with routine registration procedures. As USCIS continues to implement digital-first solutions, applicants should remain proactive in understanding their obligations, seeking guidance when necessary, and ensuring they meet all requirements to maintain lawful presence in the United States.







Comments
MWAKILISHI , WE ALREADY KNOW.
Permalink
MWAKILISHI , WE ALREADY KNOW.
Add new comment